By Andre He, Vivek Myers
A longstanding objective of the sphere of robotic studying has been to create generalist brokers that may carry out duties for people. Pure language has the potential to be an easy-to-use interface for people to specify arbitrary duties, however it’s tough to coach robots to comply with language directions. Approaches like language-conditioned behavioral cloning (LCBC) practice insurance policies to immediately imitate skilled actions conditioned on language, however require people to annotate all coaching trajectories and generalize poorly throughout scenes and behaviors. In the meantime, current goal-conditioned approaches carry out significantly better at basic manipulation duties, however don’t allow straightforward job specification for human operators. How can we reconcile the benefit of specifying duties by LCBC-like approaches with the efficiency enhancements of goal-conditioned studying?
Conceptually, an instruction-following robotic requires two capabilities. It must floor the language instruction within the bodily atmosphere, after which have the ability to perform a sequence of actions to finish the supposed job. These capabilities don’t should be discovered end-to-end from human-annotated trajectories alone, however can as an alternative be discovered individually from the suitable knowledge sources. Imaginative and prescient-language knowledge from non-robot sources will help study language grounding with generalization to various directions and visible scenes. In the meantime, unlabeled robotic trajectories can be utilized to coach a robotic to succeed in particular objective states, even when they aren’t related to language directions.
Conditioning on visible targets (i.e. objective photos) offers complementary advantages for coverage studying. As a type of job specification, targets are fascinating for scaling as a result of they are often freely generated hindsight relabeling (any state reached alongside a trajectory generally is a objective). This permits insurance policies to be skilled through goal-conditioned behavioral cloning (GCBC) on giant quantities of unannotated and unstructured trajectory knowledge, together with knowledge collected autonomously by the robotic itself. Objectives are additionally simpler to floor since, as photos, they are often immediately in contrast pixel-by-pixel with different states.
Nonetheless, targets are much less intuitive for human customers than pure language. Generally, it’s simpler for a consumer to explain the duty they need carried out than it’s to offer a objective picture, which might possible require performing the duty in any case to generate the picture. By exposing a language interface for goal-conditioned insurance policies, we are able to mix the strengths of each goal- and language- job specification to allow generalist robots that may be simply commanded. Our technique, mentioned under, exposes such an interface to generalize to various directions and scenes utilizing vision-language knowledge, and enhance its bodily expertise by digesting giant unstructured robotic datasets.
Objective representations for instruction following
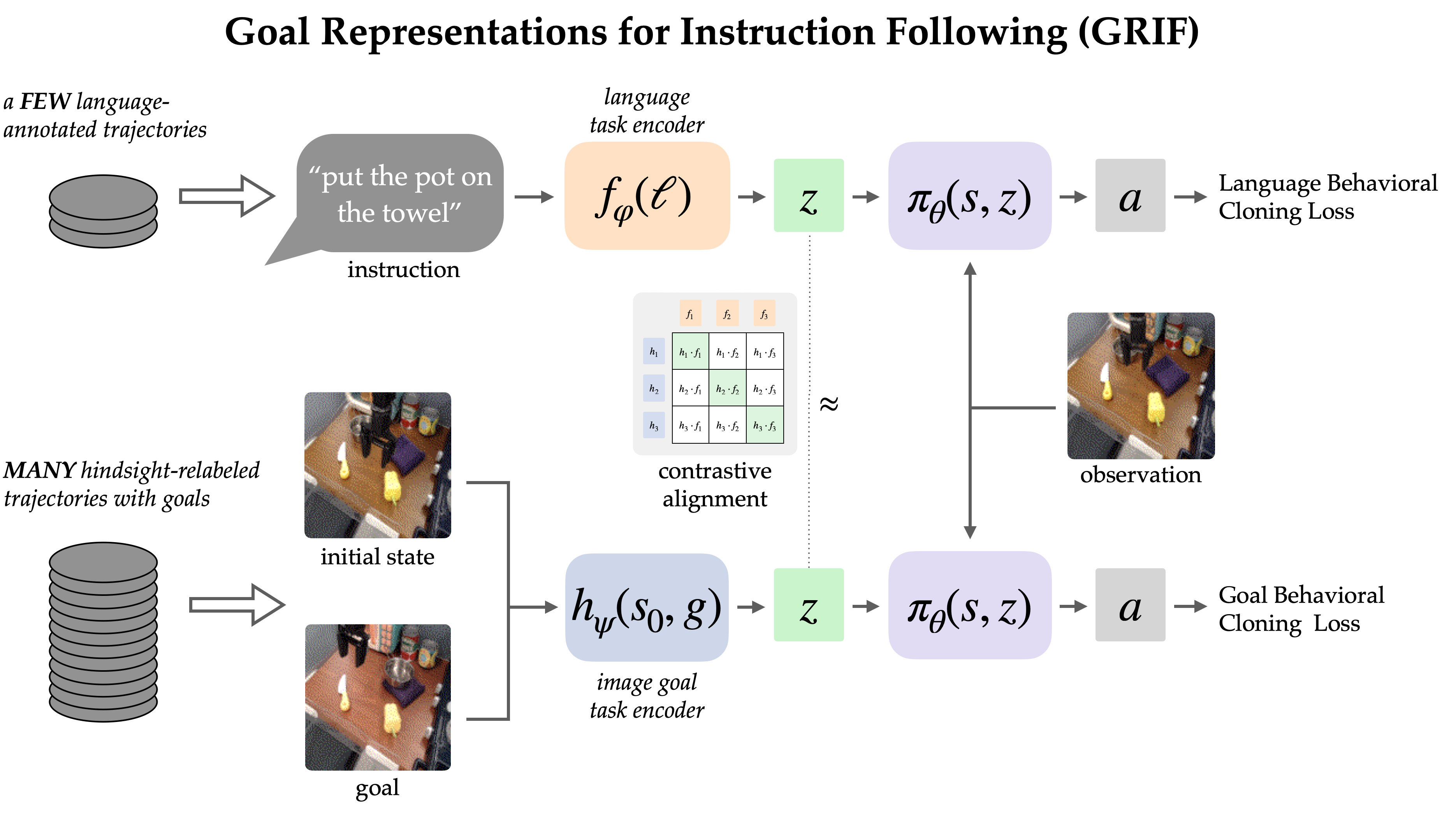
The GRIF mannequin consists of a language encoder, a objective encoder, and a coverage community. The encoders respectively map language directions and objective photos right into a shared job illustration area, which situations the coverage community when predicting actions. The mannequin can successfully be conditioned on both language directions or objective photos to foretell actions, however we’re primarily utilizing goal-conditioned coaching as a approach to enhance the language-conditioned use case.
Our strategy, Objective Representations for Instruction Following (GRIF), collectively trains a language- and a goal- conditioned coverage with aligned job representations. Our key perception is that these representations, aligned throughout language and objective modalities, allow us to successfully mix the advantages of goal-conditioned studying with a language-conditioned coverage. The discovered insurance policies are then in a position to generalize throughout language and scenes after coaching on principally unlabeled demonstration knowledge.
We skilled GRIF on a model of the Bridge-v2 dataset containing 7k labeled demonstration trajectories and 47k unlabeled ones inside a kitchen manipulation setting. Since all of the trajectories on this dataset needed to be manually annotated by people, having the ability to immediately use the 47k trajectories with out annotation considerably improves effectivity.
To study from each kinds of knowledge, GRIF is skilled collectively with language-conditioned behavioral cloning (LCBC) and goal-conditioned behavioral cloning (GCBC). The labeled dataset comprises each language and objective job specs, so we use it to oversee each the language- and goal-conditioned predictions (i.e. LCBC and GCBC). The unlabeled dataset comprises solely targets and is used for GCBC. The distinction between LCBC and GCBC is only a matter of choosing the duty illustration from the corresponding encoder, which is handed right into a shared coverage community to foretell actions.
By sharing the coverage community, we are able to count on some enchancment from utilizing the unlabeled dataset for goal-conditioned coaching. Nonetheless,GRIF allows a lot stronger switch between the 2 modalities by recognizing that some language directions and objective photos specify the identical habits. Specifically, we exploit this construction by requiring that language- and goal- representations be related for a similar semantic job. Assuming this construction holds, unlabeled knowledge also can profit the language-conditioned coverage because the objective illustration approximates that of the lacking instruction.
Alignment by contrastive studying
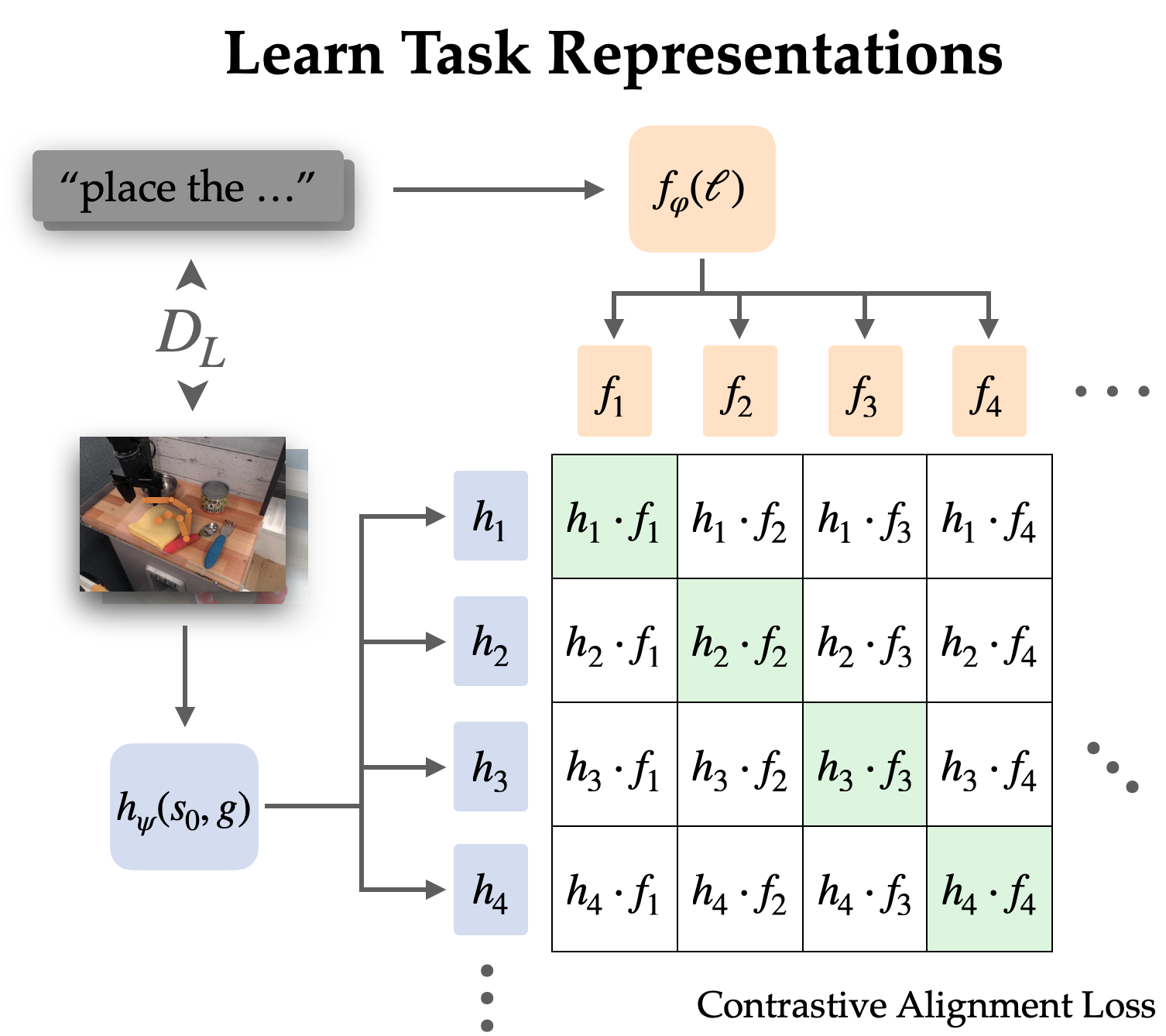
We explicitly align representations between goal-conditioned and language-conditioned duties on the labeled dataset by contrastive studying.
Since language usually describes relative change, we select to align representations of state-goal pairs with the language instruction (versus simply objective with language). Empirically, this additionally makes the representations simpler to study since they will omit most data within the photos and concentrate on the change from state to objective.
We study this alignment construction by an infoNCE goal on directions and pictures from the labeled dataset. We practice twin picture and textual content encoders by doing contrastive studying on matching pairs of language and objective representations. The target encourages excessive similarity between representations of the identical job and low similarity for others, the place the damaging examples are sampled from different trajectories.
When utilizing naive damaging sampling (uniform from the remainder of the dataset), the discovered representations usually ignored the precise job and easily aligned directions and targets that referred to the identical scenes. To make use of the coverage in the actual world, it’s not very helpful to affiliate language with a scene; moderately we want it to disambiguate between totally different duties in the identical scene. Thus, we use a tough damaging sampling technique, the place as much as half the negatives are sampled from totally different trajectories in the identical scene.
Naturally, this contrastive studying setup teases at pre-trained vision-language fashions like CLIP. They reveal efficient zero-shot and few-shot generalization functionality for vision-language duties, and provide a method to incorporate information from internet-scale pre-training. Nonetheless, most vision-language fashions are designed for aligning a single static picture with its caption with out the flexibility to grasp modifications within the atmosphere, they usually carry out poorly when having to concentrate to a single object in cluttered scenes.
To deal with these points, we devise a mechanism to accommodate and fine-tune CLIP for aligning job representations. We modify the CLIP structure in order that it will probably function on a pair of photos mixed with early fusion (stacked channel-wise). This seems to be a succesful initialization for encoding pairs of state and objective photos, and one which is especially good at preserving the pre-training advantages from CLIP.
Robotic coverage outcomes
For our fundamental outcome, we consider the GRIF coverage in the actual world on 15 duties throughout 3 scenes. The directions are chosen to be a mixture of ones which can be well-represented within the coaching knowledge and novel ones that require some extent of compositional generalization. One of many scenes additionally options an unseen mixture of objects.
We evaluate GRIF in opposition to plain LCBC and stronger baselines impressed by prior work like LangLfP and BC-Z. LLfP corresponds to collectively coaching with LCBC and GCBC. BC-Z is an adaptation of the namesake technique to our setting, the place we practice on LCBC, GCBC, and a easy alignment time period. It optimizes the cosine distance loss between the duty representations and doesn’t use image-language pre-training.
The insurance policies have been inclined to 2 fundamental failure modes. They’ll fail to grasp the language instruction, which leads to them making an attempt one other job or performing no helpful actions in any respect. When language grounding isn’t strong, insurance policies would possibly even begin an unintended job after having finished the fitting job, because the unique instruction is out of context.
Examples of grounding failures

“put the mushroom within the steel pot”

“put the spoon on the towel”

“put the yellow bell pepper on the fabric”

“put the yellow bell pepper on the fabric”
The opposite failure mode is failing to control objects. This may be as a result of lacking a grasp, shifting imprecisely, or releasing objects on the incorrect time. We be aware that these usually are not inherent shortcomings of the robotic setup, as a GCBC coverage skilled on the complete dataset can constantly reach manipulation. Relatively, this failure mode usually signifies an ineffectiveness in leveraging goal-conditioned knowledge.
Examples of manipulation failures

“transfer the bell pepper to the left of the desk”

“put the bell pepper within the pan”

“transfer the towel subsequent to the microwave”
Evaluating the baselines, they every suffered from these two failure modes to totally different extents. LCBC depends solely on the small labeled trajectory dataset, and its poor manipulation functionality prevents it from finishing any duties. LLfP collectively trains the coverage on labeled and unlabeled knowledge and reveals considerably improved manipulation functionality from LCBC. It achieves cheap success charges for frequent directions, however fails to floor extra complicated directions. BC-Z’s alignment technique additionally improves manipulation functionality, possible as a result of alignment improves the switch between modalities. Nonetheless, with out exterior vision-language knowledge sources, it nonetheless struggles to generalize to new directions.
GRIF reveals one of the best generalization whereas additionally having sturdy manipulation capabilities. It is ready to floor the language directions and perform the duty even when many distinct duties are attainable within the scene. We present some rollouts and the corresponding directions under.
Coverage Rollouts from GRIF

“transfer the pan to the entrance”

“put the bell pepper within the pan”

“put the knife on the purple material”

“put the spoon on the towel”
Conclusion
GRIF allows a robotic to make the most of giant quantities of unlabeled trajectory knowledge to study goal-conditioned insurance policies, whereas offering a “language interface” to those insurance policies through aligned language-goal job representations. In distinction to prior language-image alignment strategies, our representations align modifications in state to language, which we present results in important enhancements over normal CLIP-style image-language alignment aims. Our experiments reveal that our strategy can successfully leverage unlabeled robotic trajectories, with giant enhancements in efficiency over baselines and strategies that solely use the language-annotated knowledge
Our technique has numerous limitations that might be addressed in future work. GRIF isn’t well-suited for duties the place directions say extra about learn how to do the duty than what to do (e.g., “pour the water slowly”)—such qualitative directions would possibly require different kinds of alignment losses that take into account the intermediate steps of job execution. GRIF additionally assumes that every one language grounding comes from the portion of our dataset that’s totally annotated or a pre-trained VLM. An thrilling route for future work could be to increase our alignment loss to make the most of human video knowledge to study wealthy semantics from Web-scale knowledge. Such an strategy might then use this knowledge to enhance grounding on language exterior the robotic dataset and allow broadly generalizable robotic insurance policies that may comply with consumer directions.
This submit is predicated on the next paper:
BAIR Weblog
is the official weblog of the Berkeley Synthetic Intelligence Analysis (BAIR) Lab.

BAIR Weblog
is the official weblog of the Berkeley Synthetic Intelligence Analysis (BAIR) Lab.


